Risk assessment in IOSH Managing Safely is a pivotal process for professionals in workplace safety management. Whether you’re new to this field or a seasoned practitioner, understanding risk assessment thoroughly is not just critical, but it also empowers you to take control of workplace safety, preparing you for your IOSH Managing Safely certification.
Understanding Risk Assessment in IOSH Managing Safely
A risk assessment involves identifying, evaluating, and addressing potential workplace hazards. It extends beyond mere compliance, aiming to cultivate proactive safety culture.
Why Risk Assessments Matter
Risk assessments are mandated by the Local Govt regulations for workplace health and safety. The risk assessments are essential not only for legal compliance but also for effectively managing and mitigating workplace risks. They are particularly critical for organizations whether small or large, emphasizing the need for a documented safety management approach. A key component of effective risk assessment is compliance with HSE regulations.
 https://greenwgroup.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Why-Risk-Assessments-Matter-400x226.jpg 400w, https://greenwgroup.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Why-Risk-Assessments-Matter.jpg 530w" alt="" width="530" height="300" />
https://greenwgroup.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Why-Risk-Assessments-Matter-400x226.jpg 400w, https://greenwgroup.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Why-Risk-Assessments-Matter.jpg 530w" alt="" width="530" height="300" />When to Conduct Risk Assessments
Regular risk assessments are essential, especially during significant workplace changes, the introduction of new equipment, or in response to near-misses and incidents. Annual reviews are recommended to ensure ongoing safety.
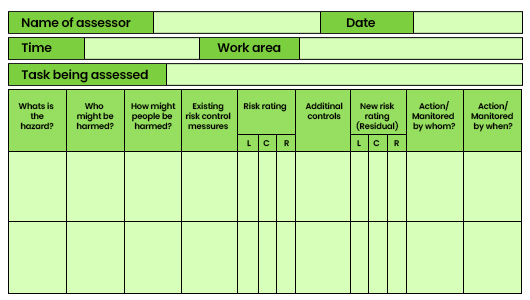
Completing the IOSH Risk Assessment Form
Select a workplace that allows you to identify hazards across categories such as mechanical, physical, chemical, environmental, biological, and organizational.
Hazard Categories in IOSH Managing Safely Syllabus
The course outlines several hazard categories that participants must understand and assess:
1. Mechanical Hazards:
These hazards involve moving machinery parts, equipment malfunctions, or other mechanical issues that can cause harm or injury to individuals working with or around such equipment.
2. Physical Hazards:
Physical hazards include factors like noise, vibration, poor lighting conditions, extreme temperatures, or ergonomic risks. If not managed properly, these hazards can lead to discomfort, injuries, or long-term health issues.
3. Chemical Hazards:
Chemical hazards involve exposure to harmful substances—solids, liquids, or gases. These substances can cause health issues ranging from irritation to severe toxic effects.
4.Environmental Hazards:
Environmental hazards encompass risks related to the workplace environment, such as slippery floors, uneven surfaces, poor air quality, or inadequate ventilation. These hazards can contribute to accidents or health problems.
5. Biological Hazards:
Biological hazards arise from exposure to bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms that cause infections or illnesses. Proper handling and hygiene practices mitigate these risks.
6. Organizational Hazards:
Organizational hazards are associated with workplace culture or organizational structure. Examples include high workload, lack of training, poor communication, or inadequate supervision. These factors can impact employee well-being and safety.
Risk Assessment Process in IOSH Managing Safely
The risk assessment process involves systematic steps that are not just important, but they also guide you through the process of identifying, evaluating, and controlling workplace hazards
 https://greenwgroup.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Risk-Assessment-Process-in-IOSH-Managing-Safely-400x81.jpg 400w, https://greenwgroup.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Risk-Assessment-Process-in-IOSH-Managing-Safely.jpg 530w" alt="" width="530" height="107" />
https://greenwgroup.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Risk-Assessment-Process-in-IOSH-Managing-Safely-400x81.jpg 400w, https://greenwgroup.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Risk-Assessment-Process-in-IOSH-Managing-Safely.jpg 530w" alt="" width="530" height="107" />
Comments